Energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time [1] to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator

Compressed air energy storage
This report investigates one type of storage, compressed air energy storage (CAES), where energy is stored by compressing air during hours of low electricity demand and later expanding

Exploring Compressed Air Storage: Technologies
The understanding of Types of Compressed Air Storage Systems is vital in grasping the overall capabilities and efficacy of compressed air technologies. Different systems come with their unique characteristics, catering to

LPO Announces Conditional Commitment for Long Duration Compressed Air
Typically, compressed air energy storage (CAES) uses surplus, low-cost electrical energy (e.g. from renewable power generation) and stores it safely as compressed air, often in

Hybrid Compressed Air/Water Energy Storage
Description Energy storage systems that can efficiently store excess off-peak energy for use at peak-demand times would promote increasing adoption of alternative energy technologies. This method stores energy in the form of

Current research and development trend of
2. Brief description of CAES systems and current development A CAES system mainly includes compressors, driving motors, generators, air reservoir (s) (underground cavern), turbines and other

Dynamic simulation of Adiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage
Energy storage has the potential to meet this challenge and enables large scale implementation of renewables. In this paper we investigated the dynamic performance of a

Compressed air energy storage technology:
Compressed air energy storage technology (CAES) is an energy storage technology that cleverly converts electrical energy into air internal energy and realizes storage and release.

Compressed air energy storage | Energy Storage for Power Systems
The application of elastic energy storage in the form of compressed air storage for feeding gas turbines has long been proposed for power utilities; a compressed air storage

Battery and compressed air energy storage system
Request PDF | Battery and compressed air energy storage system - concept description | One of the electric power industry problems is unstable electricity generation by

Cogeneration systems of solar energy integrated with compressed air
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) is considered to be one of the most promising large-scale energy storage technologies to address the challenges of source-grid

Energy storage
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time [1] to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is

Schematic description of a compressed air energy
Lined rock cavern at shallow depth is identified as a promising alternative and cost-effective solution for air storage of large-scale compressed air energy storage (CAES) plant. To better

(PDF) Comprehensive Review of Compressed Air
As a result, integrating an energy storage system (ESS) into renewable energy systems could be an effective strategy to provide energy systems with economic, technical, and environmental benefits.

Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES): A
By storing vast amounts of energy in geological formations, depleted gas reservoirs, or even specially designed vessels, CAES systems can provide gigawatt-scale storage over extended durations—from hours

Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES):
Compressed Air Energy Storage is a technology that stores energy by using electricity to compress air and store it in large underground caverns or tanks. When energy is needed, the compressed air is released,

Compressed Air Energy Storage: Types, systems and applications
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) is a technology employed for decades to store electrical energy, mainly on large-scale systems, whose advances have been based on

(PDF) Energy Storage Systems: A Comprehensive
This book thoroughly investigates the pivotal role of Energy Storage Systems (ESS) in contemporary energy management and sustainability efforts. Starting with the essential significance and

Compressed air energy storage | PPT | Power and
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) stores energy by using excess electricity to compress and pump air into underground storage facilities such as salt caverns. The stored air is later released to drive turbines and

Advanced Compressed Air Energy Storage Systems:
The comparison and discussion of these CAES technologies are summarized with a focus on technical maturity, power sizing, storage capacity, operation pressure, round

Small-scale adiabatic compressed air energy storage: Control
A small-scale Adiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage system with an artificial air vessel has been analysed and different control strategies have been simulated and

Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) is a way to store energy generated at one time for use at another time. At utility scale, energy generated during periods of low energy demand (off-peak) can be released to meet higher

Compressed Air Energy Storage: Types, systems and applications
In thermo-mechanical energy storage systems like compressed air energy storage (CAES), energy is stored as compressed air in a reservoir during off-peak periods, while it is used on

Compressed Air Energy Storage as a Battery
The recent increase in the use of carbonless energy systems have resulted in the need for reliable energy storage due to the intermittent nature of renewables. Among the existing energy storage

Compressed air energy storage
CAES takes the energy delivered to the system (by wind power for example) to run an air compressor, which pressurizes air and pushes it underground into a natural storage area such as an underground salt cavern.

Compressed Air Energy Storage
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) offers several advantages over other energy storage technologies, making it a compelling choice for large-scale energy management. It relies on

Compressed Air Energy Storage Types, Systems
The document is a comprehensive overview of Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES), detailing its types, systems, and applications. It includes discussions on isothermal and adiabatic CAES, technical feasibility, and

What is energy storage?
Energy storage is the capturing and holding of energy in reserve for later use. Energy storage solutions for electricity generation include pumped-hydro storage, batteries, flywheels, compressed-air

Modelling and experimental validation of advanced adiabatic compressed
Advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage (AA-CAES) has been recognised as a promising approach to boost the integration of renewables in the form of

mechAnicAl energy storAge
A. Physical principles An Adiabatic Compressed Air Energy Storage (A-CAES) System is an energy storage system based on air compression and air storage in geological underground

The role of compressed air energy storage (CAES) in
Future sustainable energy systems call for the introduction of integrated storage technologies. One of these technologies is compressed air energy storage (CAES). In
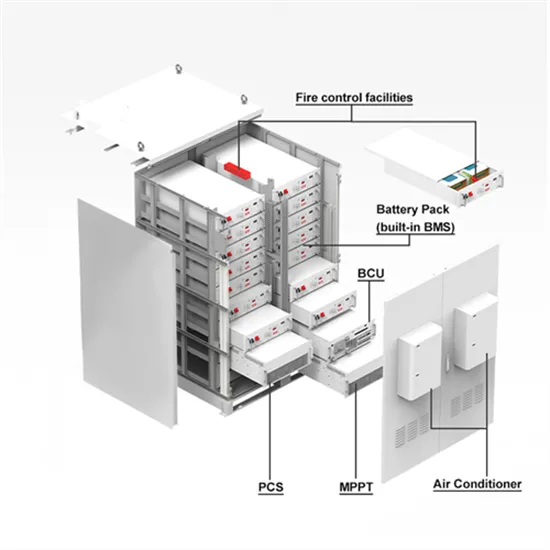
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES)
Technical Description Types of Systems Adiabatic CAES (A-CAES) stores the heat of compression created during the charging process in a thermal energy storage system, and reuses it during the expansion, or discharging

Microsoft Word
The uses for this work include: Inform DOE-FE of range of technologies and potential R&D. Perform initial steps for scoping the work required to analyze and model the benefits that could

A comprehensive performance comparison between compressed air energy
Currently, working fluids for adiabatic compressed energy storage primarily rely on carbon dioxide and air. However, it remains an unresolved issue to which of these two
You might like this video
6 FAQs about [Compressed air energy storage system description]
What is compressed air storage (CAES)?
A pressurized air tank used to start a diesel generator set in Paris Metro Compressed-air-energy storage (CAES) is a way to store energy for later use using compressed air. At a utility scale, energy generated during periods of low demand can be released during peak load periods.
How many large scale compressed air energy storage facilities are there?
As of late 2012, there are three existing large scale compressed air energy storage facilities worldwide. All three current CAES projects use large underground salt caverns to store energy. The first is located in Huntorf, Germany, and was completed in 1978.
What is compressed air energy storage?
Compressed-air energy storage can also be employed on a smaller scale, such as exploited by air cars and air-driven locomotives, and can use high-strength (e.g., carbon-fiber) air-storage tanks.
What is a compressed air energy storage plant?
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) plants are largely equivalent to pumped-hydro power plants in terms of their applications. But, instead of pumping water from a lower to an upper pond during periods of excess power, in a CAES plant, ambient air or another gas is compressed and stored under pressure in an underground cavern or container.
What are the advantages of compressed air energy storage (CAES)?
Advantages of Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) 1. Large-Scale Storage: CAES systems are capable of storing vast amounts of energy, making them ideal for grid-scale applications. They are especially useful in combination with wind farms, where large quantities of excess energy may be generated during windy periods. 2.
How does a compressed air system work?
Contrasted with traditional batteries, compressed-air systems can store energy for longer periods of time and have less upkeep. Energy from a source such as sunlight is used to compress air, giving it potential energy.
Related Contents
- Foreign compressed air energy storage team cooperation
- Bid for iraq compressed air energy storage project
- Compressed air energy storage project investment cost
- Compressed air energy storage in oil and gas reservoirs
- Us compressed air energy storage power station bidding
- On compressed air energy storage technology

